How To Improve Water Availability In India
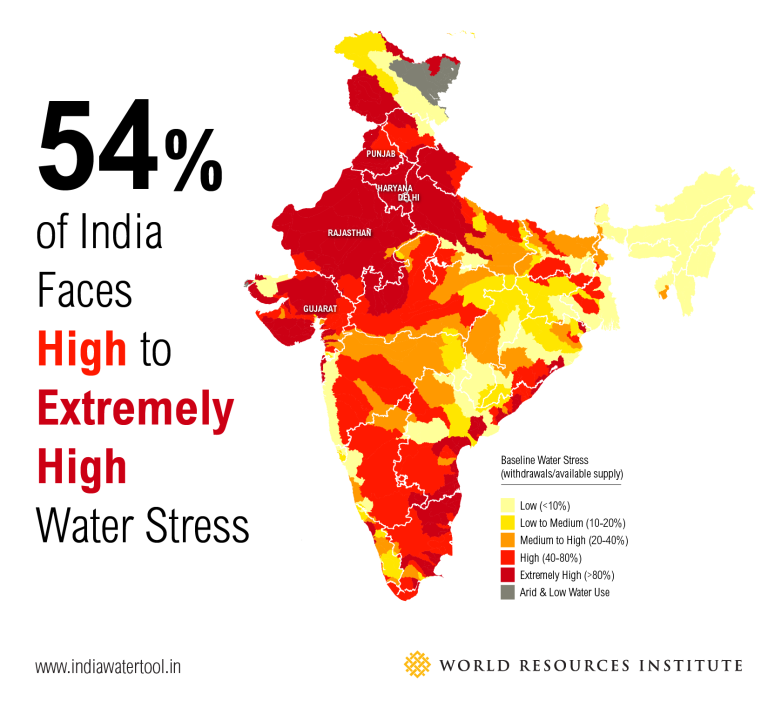
Water plays a critical role in sustaining societies, economies, and ecosystems—but it’s becoming increasingly scarce despite the growing demand. Experts predict that by 2030, global freshwater demand will outpace supply by 40% to 50%. For countries like India—now the world’s most populous nation—these stats are not encouraging. So, how do we improve water availability in India?
India is already struggling to provide all its citizens with sustainable and equitable access to water resources. In fact, even though 18% of the world’s population resides in India, the country only has enough water resources to sustain 4% of its people. This reality makes India the most water-stressed country despite its vast rivers and underground aquifers.
For India to have a more sustainable future, three key players need to be involved: industries, municipal water corporations, and consulting engineers. If you fall into one of these categories, you must implement three strategic steps to help improve water availability in India. However, these steps are not general ideas or loose suggestions that may work—instead, they are directly tied to the main factors contributing to India’s challenges with water availability.
Top Reasons for Water Scarcity in India
There are various reasons why water scarcity in India is so prevalent. From interstate water disputes to poor water infrastructure, many factors feed into the country’s water resource challenges. However, three specific issues have the biggest impact on India’s water availability and capacity to meet current and future demands.
1. Contamination and Pollution
India continues to urbanize and grow. While that’s great, the country’s water bodies are becoming increasingly toxic. Research suggests that around 70% of India’s surface water sources are unfit for consumption. It’s also estimated that nearly 40 million liters of wastewater flow into India’s rivers, tributaries, lakes, and other water sources, but only a small fraction is effectively treated.
With contaminated and polluted water bodies, India has few clean water resources to sustain its economy, ecosystem, and civil society. The impact of this reality is significant. According to an article by the World Economic Forum, environmental degradation is costing India the equivalent of around $80 billion US dollars annually. The health costs stemming from water pollution is up to the equivalent of $8.7 billion US dollars per year—and the number of lives lost annually in India because of water scarcity, hygiene, and sanitation is around 400,000 people.
2. Depleting Groundwater
For most people in India, groundwater is the only source of water, enabling citizens to meet some of their domestic and agricultural needs. However, because India has such a large population, the widespread extraction of water has resulted in a noticeable decline of these resources and an increases of salinity in such resources.
According to the World Bank, almost 63% of India’s districts are experiencing decreasing groundwater levels. Poverty rates where districts’ groundwater tables have fallen below eight meters (8 M) are also high, coming in at 9% to 10%, making small farmers incredibly vulnerable to these effects. If water availability does not improve in India, at least 25% of the country’s agriculture will be at risk.
3. The Climate Crisis
Monsoons have long been a water source for India, but climate change is leading to unpredictable floods and droughts, both of which are exacerbating water scarcity conditions. For example, while India is experiencing more days with heavy rainfall, the country is seeing longer dry spells in between these monsoon storms. One area that is particularly impacted is India’s central belt, which encompasses western Maharashtra State and the Bay of Bengal. Over the last 70 years, extreme rainfall events have increased threefold—but total annual rainfall has decreased.
Additionally, the Himalayan region is also at risk because of climate change. In the past, this mountain range helped protect India from droughts. However, a 2019 report suggests that at least one-third of the glaciers is anticipated to cease to exist by 2100. While that seems far off, the impact of glacial melting is already apparent. Glaciers are currently melting in the Himalayas and contributing to floods and droughts in India.
Remediate, Desalinate, Reuse
Improving water availability in India will be challenging for industries, municipal water corporations, and consulting engineers who assist these clients with these challenges. This is especially apparent since the country is already experiencing severe water scarcity due to complex factors.
However, taking a step in the right direction is possible if the main players continue to implement three strategies:
Remediate surface water sources,
Desalinate water sources,
Treat & Reuse wastewater sources.
Each of the suggested steps is crucial. The first two play a role in decontaminating water bodies so that they are clean and safe enough to utilize—and the third helps improve India’s water supply so that the country can meet its current and future water demands. By utilizing these strategies, industries, municipal water corporations, and consulting engineers who work with these organizations can tackle the three biggest factors contributing to India’s water scarcity.
However, effective implementation will require these key players to approach each step in a specific way and with appropriate strategic technical partners.
1. Remediate Surface Water Sources
For India to effectively remediate its surface water sources, industries, municipal water corporations, and consulting engineers must have the right tools. One of the best is an enzyme treatment such as Zeozyme. This solution is a powder or liquid formulation that can improve the water quality in lakes and better remediate tertiary wastewater. Once it’s put into a water source, the enzymatic treatment is activated.
Additionally, adding a sustainable, bio-organic liquid flocculant solution such as Zeoturb to the surface water source is best, as it will help with the flocculation and clarification of the water. It will also reduce and remove inorganic and organic matter like certain dyes, silt, algae, sediment, and trace heavy metals .
Both of these solutions can work synergistically together or in association with other catalysts based on the treatment application.
2. Desalinate Surface Water Sources
After starting the remediation process, desalination for higher salinity water sources would be a logical next step. Implementing this will help further remove contaminants like nutrients and salinity from surface and seawater sources. Industrial companies, in particular, should use a desalination process on their process water or tertiary water treatment operations to have the most significant impact in creating clean, safe water where higher salinity levels are common.
Additionally, to ensure the desalination process goes well, it’s important to use an advanced method that checks a few boxes, like the following:
Energy-efficient
Environmentally conscious
Includes low-fouling Nano Composite RO Membrane Technology
It achieves post-remineralization and disinfection using solutions such as Genclean-Muni as required
By checking these boxes, the desalination process in association with optimized pretreatment will help India reduce its carbon footprint—mitigating the climate crisis spurring the country’s water scarcity—while effectively treating its surface water sources to improve water availability.
3. Reuse Water
Also known as water recycling or water reclamation, water reuse is all about reusing treated wastewater. The reused water can be utilized for various purposes, including groundwater replenishment, agriculture and irrigation, and environmental restoration, all of which can benefit India’s economy, ecosystem, and society as a whole.
Still, the most important thing to consider to ensure this step is completed successfully is the type of water reuse process that is utilized. It is imperative to employ advanced, sustainable, and eco-friendly techniques to ensure a long-term and reliable water supply is available.
Expertise Matters
Water scarcity is such a prevalent issue in India that it cannot be tackled without the right team in place. Wastewater and water experts must be a part of the solution for change to truly happen. So, if you work for an industry, municipal water corporation or are a consulting engineer in India, you should find experienced technical partners to assist and collaborate in this area.
Our team at Genesis Water Technologies has years of experience, expertise, and innovative solutions to ensure every step suggested in this article is implemented effectively to provide results. Our advanced treatments including Genclean AOP – our liquid AOP disinfection solutions along with GWT ZeoTurb—a non-toxic, sustainable bio-flocculant—will remediate surface water and wastewater sources. Our desalination solutions will further decontaminate water through polishing salts removal, and our unique water reuse process will ensure India has sustainable clean sources of water over the long-term.
We can help India get on track to meet current and future water demand. Contact our Irygen Water Solutions office in India or reach to our local channel partners in India to assist your organization anywhere across the Indian subcontinent.
Contact our water & wastewater treatment experts at Genesis Water Technologies at +1-321 280 2742 or via email at customersupport@genesiswatertech.com for a free initial consultation or to engage further to discuss your treatment issues and requirements

